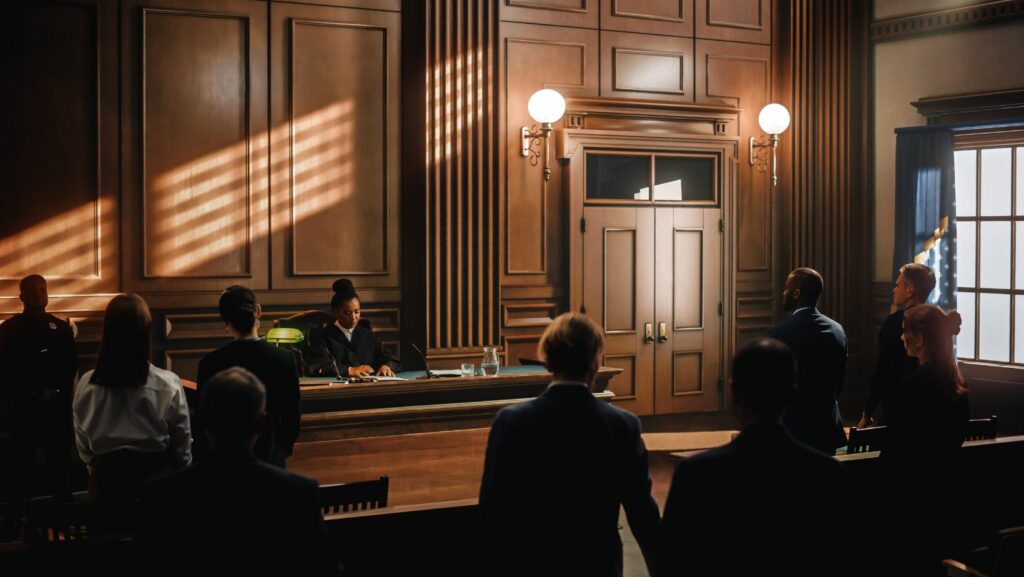
As an expert in the legal field, I’ll provide you with a clear and concise answer to the question: which is a true statement about federal judges? Federal judges are appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by the Senate. This means that their selection process involves both executive and legislative branches of government. Unlike state judges who are typically elected, federal judges serve lifetime appointments, ensuring their independence from political pressures.
Another true statement about federal judges is that they play a crucial role in interpreting and applying the law within the federal court system. They preside over cases involving constitutional issues, federal laws, and disputes between states or individuals from different states. Their decisions have far-reaching implications on society as they establish legal precedents that shape future rulings.
Which Is a True Statement About Federal Judges?
The process of appointing federal judges is a crucial aspect of ensuring the integrity and effectiveness of the judiciary system. Federal judges are appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by the Senate, following Article II, Section 2 of the U.S. Constitution. This appointment process serves to uphold the principle of checks and balances within our government.
During this process, potential candidates are carefully vetted based on their qualifications, experience, and legal expertise. They undergo a rigorous evaluation to determine their suitability for judicial office. This includes analyzing their educational background, professional accomplishments, and ethical conduct.
Educational and Professional Background
To become a federal judge, individuals must possess a strong educational foundation in law. Most federal judges have earned a Juris Doctor (J.D.) degree from an accredited law school. Additionally, many judges have gained valuable experience through clerkships with other judges or legal practice in specialized areas such as constitutional law or corporate litigation.
Furthermore, possessing extensive professional experience enhances a candidate’s qualifications for federal judgeship. Many successful nominees have distinguished themselves as practicing attorneys or legal scholars before being considered for judicial appointments. This practical knowledge equips them with insights into complex legal issues they may encounter while serving on the bench.
Experience in the Legal Field
Experience within the legal field is highly valued when selecting federal judges since it provides them with a comprehensive understanding of legal principles and procedures. Candidates who have demonstrated excellence in their previous roles as attorneys or jurists are more likely to be considered for nomination.
Moreover, diversity in professional experiences brings varied perspectives to the judiciary system. A range of backgrounds – such as criminal prosecution or defense work, civil litigation expertise, or public service – enriches the collective wisdom on which sound judgments are built.

Appointment Process for Federal Judges
Nomination by the President
The appointment process for federal judges begins with the nomination by the President of the United States. When a vacancy arises in a federal court, whether it’s a district court, circuit court, or even the Supreme Court, the President has the authority to select and nominate a candidate to fill that position. This is an important responsibility of the executive branch and allows the President to shape the judiciary according to their own legal philosophy.
The President’s nomination is typically based on various factors such as qualifications, experience, and ideology. The selected nominee may have an extensive background in law or come from diverse legal backgrounds such as private practice, academia, or public service. It is crucial for presidents to carefully consider their choices as these appointments can have long-lasting impacts on American jurisprudence.
Senate Confirmation Process
Once nominated by the President, federal judge candidates must go through a rigorous confirmation process in the Senate. The Constitution grants senators with “advice and consent” powers when it comes to judicial nominations. This means that they have an influential role in deciding whether a nominee should be confirmed.
During this process, nominees often face scrutiny from both political parties and are subject to thorough vetting by Senate committees. These committees analyze nominees’ qualifications, past rulings (if applicable), and conduct interviews before making recommendations to their fellow senators. The confirmation vote takes place on the Senate floor where a simple majority is required for approval.