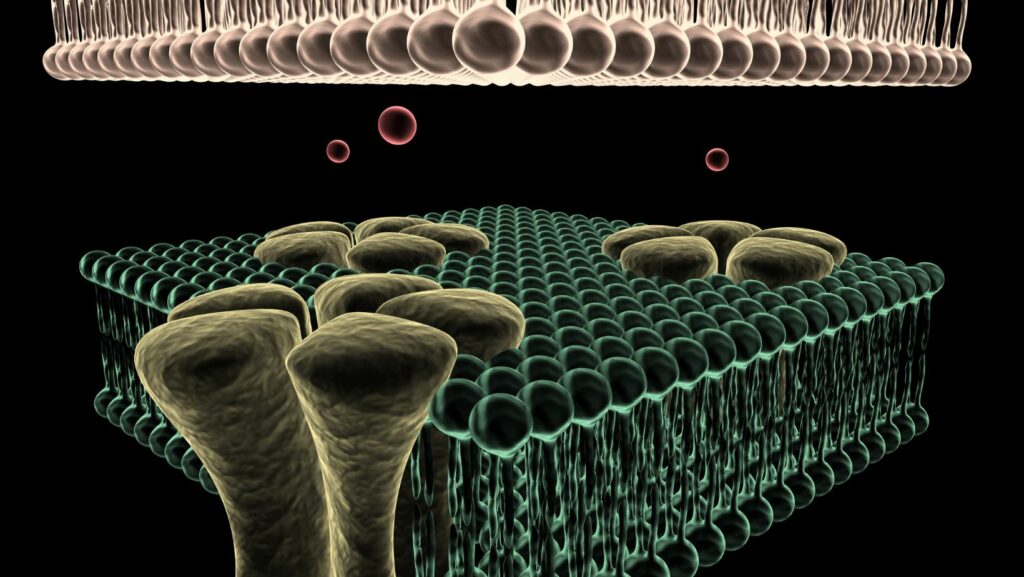
Ions Required for Cell Function and Survival
I’ve always been fascinated by the intricate workings of cells and how they are able to carry out their functions with such precision. One crucial aspect of cell function and survival lies in the presence of ions. These charged particles play a vital role in maintaining the balance and integrity of cells, ensuring that they can perform their necessary tasks. In this article, I’ll delve into the specific ions that are required for cell function and survival, highlighting their importance and the ways in which they contribute to cellular processes.
When it comes to cell function, ions serve as essential messengers and regulators. They facilitate communication between cells, allowing for the transmission of signals and coordination of various biological processes. From the movement of ions across cell membranes to the activation of enzymes, these charged particles are involved in a wide range of cellular activities.
Importance of Ions in Cell Function and Survival
Ions play a crucial role in the proper functioning and survival of cells. The presence and proper balance of specific ions are essential for maintaining cellular communication, as well as the electrochemical balance within cells. Let me explain the importance of ions in more detail.
Role of Ions in Cellular Communication
Cellular communication is a fundamental process that allows cells to coordinate their activities and respond to external stimuli. Ions, such as sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), calcium (Ca2+), and chloride (Cl-), act as messengers and regulators in this intricate network.
Sodium (Na+) and Potassium (K+) – Sodium and potassium ions are vital for the generation and propagation of electrical signals in nerve cells. This process, known as action potential, is crucial for the transmission of information throughout the nervous system. Without the proper balance of these ions, nerve cells would struggle to communicate effectively, impairing various bodily functions.
Calcium (Ca2+) – Calcium ions are involved in a wide range of cellular processes, such as muscle function, hormone secretion, and gene expression. They act as secondary messengers, relaying signals from the cell surface to its interior. Inadequate calcium levels can lead to disruptions in these processes, compromising the overall function and survival of cells.
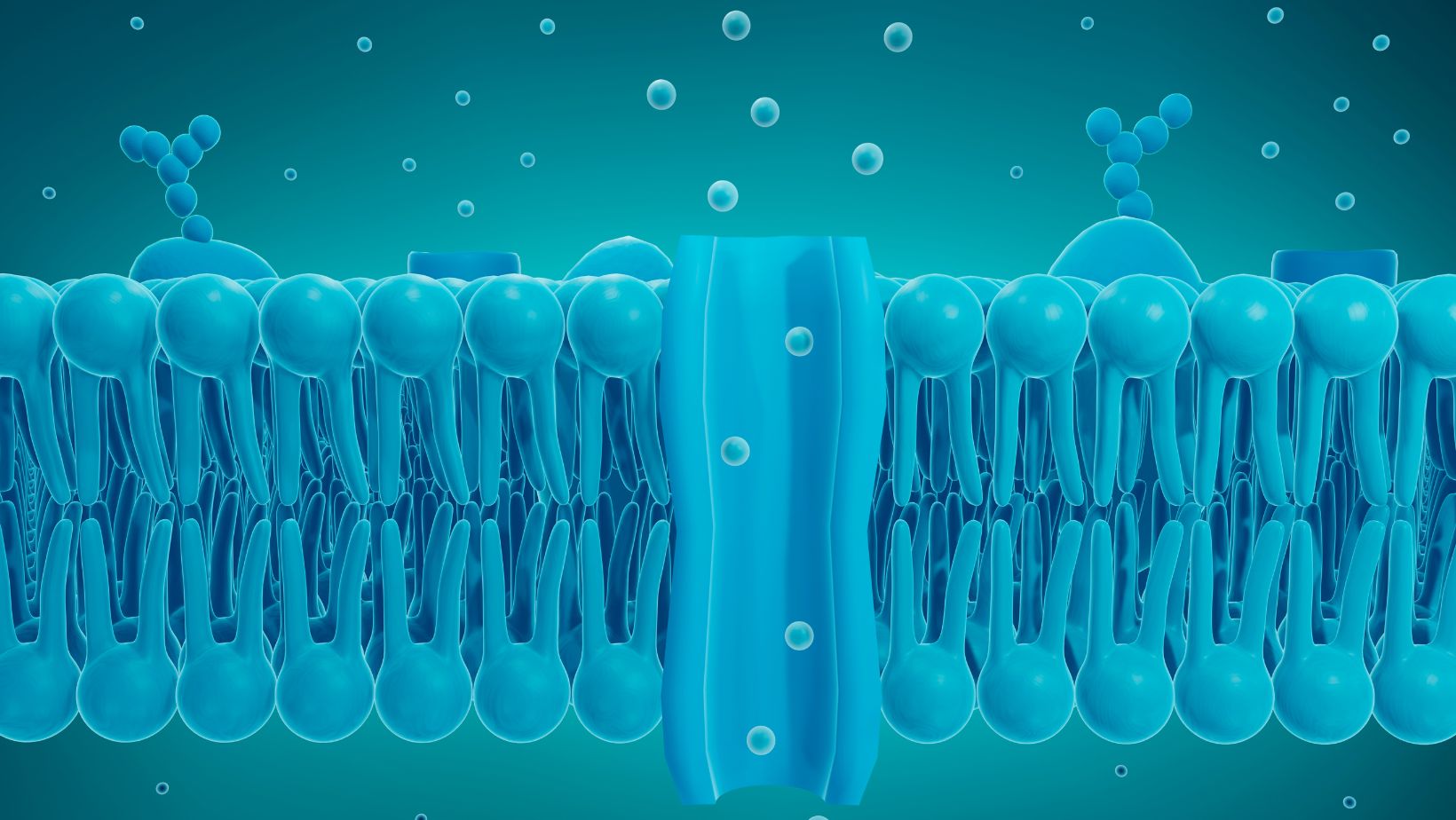
Essential Ions for Cell Function
As an expert in cell biology, I understand the crucial role that ions play in the survival and proper functioning of cells. These charged particles are not only messengers but also regulators, coordinating biological processes and facilitating communication between cells. In this section, I will dive deeper into the essential ions that are required for cell function and survival.
Sodium (Na+)
Sodium (Na+) is one of the most essential ions for cell function. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the osmotic balance of cells, controlling the movement of water and nutrients. Additionally, sodium is a key player in generating electrical signals in nerve cells, which are vital for transmitting information throughout the body. Without the presence of sodium ions, cells would struggle to efficiently carry out their functions, leading to significant disruptions in cell activity.
Potassium (K+)
Potassium (K+) is another essential ion for cell function and survival. Similar to sodium, potassium helps maintain the osmotic balance in cells and assists in the transmission of electrical signals. In fact, potassium ions are responsible for repolarizing nerve cells after an action potential, allowing them to transmit multiple signals rapidly. This process is fundamental to the proper functioning of the nervous system and other processes such as muscle contraction.
Calcium (Ca2+)
Calcium (Ca2+) is a versatile ion that is involved in various cellular functions. It acts as a crucial second messenger, relaying signals from the extracellular environment to the cell’s interior. This ion regulates processes such as muscle contraction, neurotransmitter release, and gene expression. Without the presence of calcium ions, cells would struggle to properly carry out these essential functions, compromising overall cell function and survival.
Magnesium (Mg2+)
Magnesium (Mg2+) is often referred to as the “forgotten ion” due to its overshadowed popularity compared to sodium, potassium, and calcium. However, magnesium is just as important for cell function and survival. It plays a critical role in enzyme function, DNA replication, and maintaining the stability of cell membranes. Additionally, magnesium is involved in the production and transfer of energy within cells. Without sufficient magnesium ions, cellular processes would be hindered, ultimately affecting the overall functionality of cells.
Conclusion
In this article, I have explored the significance of ions in cell function and survival. Ions play a crucial role in maintaining the osmotic balance of cells, generating electrical signals in nerve cells, and regulating various cellular processes. Without the proper balance and availability of ions such as sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, phosphate, and bicarbonate, cells would struggle to carry out their functions efficiently, compromising their survival and overall functionality.